The nutritional differences between cow milk and goat milk
When comparing goat milk vs cow milk, the difference starts with digestibility. Goat milk is known for being naturally easier to digest. This is mainly due to the lower levels of αs1-casein found in goat milk. In contrast, cow’s milk contains significantly more of this protein, which is one of the main triggers for milk allergies. So if your customers are looking for a milk alternative that’s less allergenic, goat milk is a strong candidate. The difference between goat and cow milk in terms of allergenic properties is scientifically recognized.
Goat milk versus cow milk: the A2 protein advantage
Another nutritional difference in the goat milk vs cow milk debate lies in the type of beta-casein protein present. Cow’s milk often contains both A1 and A2 β-casein. A1 β-casein has been associated with digestive discomfort and other disturbances. Goat milk, however, naturally contains only A2 β-casein. This A2 profile contributes to better digestive comfort, making goat milk a smart choice for consumers with sensitive stomachs. When evaluating if goat or cow milk is healthier, the exclusive presence of A2 β-casein in goat milk is a significant advantage.
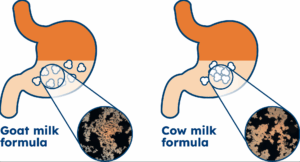
Goat milk vs cow milk: softer curds, smoother digestion
The way milk behaves in the stomach also matters. Goat milk forms softer and looser curds due to its low αs1-casein content. In contrast, cow’s milk produces firmer curds that are more difficult to break down. Softer curds in goat milk mean a smoother passage through the digestive system. This feature is particularly beneficial for infants, elderly individuals, or anyone with a compromised digestive system. This difference between goat and cow milk can play a crucial role in nutritional planning for vulnerable groups.
Goat milk vs cow milk: whey protein that’s easier to digest
Whey proteins are another key difference in goat milk vs cow milk. Goat milk contains whey proteins like β-lactoglobulin, which are more easily digested than those found in cow’s milk. This means less strain on the digestive system and better nutrient absorption. The lactose in goat milk vs cow milk can also affect digestibility, with some evidence suggesting that goat milk may be better tolerated in mild lactose sensitivity cases. For companies in India seeking milk ingredients for sensitive populations, this is a crucial advantage.
Why goat milk is a smarter choice for bulk buyers
Businesses that produce dairy products for sensitive consumers, including infants, children, or the elderly, will benefit from the natural composition of goat milk. The lower allergenic potential, better digestibility, and unique protein structure give goat milk a nutritional profile that meets growing consumer demands for healthier and gentler alternatives to cow’s milk. When assessing if goat or cow milk is healthier, goat milk’s digestive and protein advantages make a compelling case.
Choosing goat milk also supports product innovation in high-demand markets such as infant nutrition, functional foods, and health supplements. Ausnutria provides high-quality bulk goat milk ingredients that retain these benefits, helping your brand deliver premium nutrition. Moreover, understanding the lactose in goat milk versus cow milk helps manufacturers make informed ingredient decisions for lactose-sensitive consumers.
In conclusion, the nutritional differences between cow’s milk and goat’s milk are significant. Goat milk offers a gentler, more digestible, and less allergenic option that aligns perfectly with the evolving needs of modern consumers. For manufacturers, this means a reliable and superior ingredient for creating next-generation dairy products. The difference between goat and cow milk is more than just composition—it’s about providing a healthier future.

